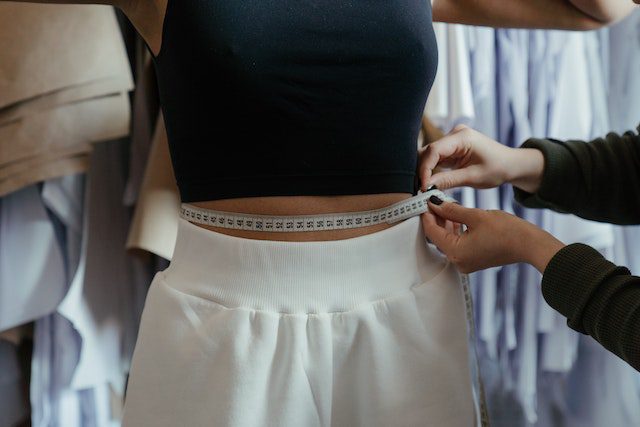
What is belly fat, and why should you be concerned about it?
Belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is a type of fat that is stored in and around the abdominal organs. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is found just under the skin, visceral fat is located deep within the abdominal cavity.
There are two types of belly fat: upper and lower. Upper belly fat is located around the stomach and upper intestines, while lower belly fat is found around the lower intestines and pelvis.
Both types of belly fat can be dangerous to your health if they are not kept under control. Upper belly fat is known as visceral fat which is more dangerous to your health. Visceral fat produces hormones and other substances which are linked with various diseases like type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, stroke, high cholesterol level, high triglycerides levels, etc. On the other hand, lower belly fat is known as subcutaneous fat which is stored under the skin. Lower belly fat is less dangerous as compared to visceral fat but can still lead to some health problems such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.








Scientists believe that this type of fat is more difficult to lose than other types of body fat. This is because it is stored deep within the abdomen and surrounds organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. As a result, it is not easily accessible by the body’s cells and requires more energy to break down.
What factors cause abdominal fat?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of belly fat. These include:


Genetics
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of how genetics affects belly fat. Everyone’s genetic makeup is different, and that means that the way our bodies store and use fat can vary from person to person. However, there are some general trends that researchers have observed when it comes to the role of genetics in belly fat. For example, people who have certain genetic mutations tend to be more likely to store fat around their midsections. In addition, certain hormones (such as testosterone and estrogen) can influence where our bodies store fat. So if you’re wondering why you can’t seem to get rid of your belly fat, your genes may be part of the reason.


Gender
There are a few ways in which gender affects belly fat. First of all, men and women tend to store fat differently. Women typically have more body fat overall, and they also tend to store more fat around the hips and thighs. Men, on the other hand, are more likely to store fat around the waist. This difference is due to hormones and body composition. Women have higher levels of estrogen, which causes them to deposit more fat around the hips and thighs. Men have higher levels of testosterone, which causes them to deposit more fat around the waist. In addition, men tend to have more muscle mass than women, which also contributes to their different patterns of fat storage. Finally, gender can affect how easy it is to lose belly fat. In general, men tend to lose weight faster than women do, but this varies depending on individual metabolism and lifestyle choices. However, both men and women can take steps to reduce their belly fat through diet and exercise.


Sedentary Lifestyle
Calories in calories out – this is the oldest and most well-known weight loss rule for a reason. Calories have to be in a deficit for weight loss to occur, meaning that you have to burn more calories than you eat. When it comes to weight loss, it doesn’t matter where those calories come from, but a sedentary lifestyle is a major factor when it comes to belly fat. If you don’t get enough exercise, your body isn’t as good at burning calories, and those calories tend to get stored as fat.


Age
Scientists have long been puzzled by the fact that belly fat seems to be more common as we age. Now, new research is beginning to shed light on why this may be the case. One theory is that changes in hormones may play a role. As we age, our bodies produce less of the hormone testosterone, which has been shown to help build muscle and burn fat. At the same time, our bodies produce more of the hormone estrogen, which has been linked to increased abdominal fat storage. Another theory is that our body becomes less effective at breaking down and metabolizing fat as we age, making it harder to lose weight. All of these factors can contribute to an increase in belly fat.


Poor Diet
A healthy diet is important for many reasons. It can help to protect against heart disease, stroke, and some forms of cancer. It can also help to keep blood sugar levels in check, reduce inflammation, and promote a healthy weight. However, a poor diet can also have noticeable effects on the body, including an increase in belly fat. There are several scientific explanations for this link between diet and belly fat. For one thing, a diet high in processed foods and added sugars are thought to contribute to weight gain and abdominal obesity. Additionally, a lack of fiber in the diet can lead to constipation, which can, in turn, cause abdominal bloating and discomfort. Finally, eating too few healthy fats can make it difficult to lose weight, even when following a healthy diet and exercising regularly. All of these factors together suggest that poor diet choices can lead to an increase in belly fat.


Stress
When we think of stress, we often associate it with mental health issues such as anxiety or depression. However, stress can also have a physical effect on our bodies, particularly in the form of belly fat. When we experience stress, our bodies release a hormone called cortisol. Cortisol is responsible for regulating our blood sugar levels, but it also promotes the storage of fat in the abdominal area. In addition, cortisol can increase our appetites, leading us to eat more than we would under normal circumstances. As a result, stress can lead to weight gain and a larger waistline.
The health risks are associated with having too much belly fat.
Excess abdominal fat is not just an aesthetic concern. It is a major health risk, linked with conditions like heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, breathing problems, etc. Below are 5 common health problems which are related to excess fat around the stomach.
One of the most serious risks associated with having too much belly fat is heart disease. Fat around the abdominal area can lead to a build-up of plaque in the arteries, which can narrow them and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Another health problem caused by belly fat is diabetes. Diabetes is a condition that occurs when your body can’t properly use insulin, a hormone that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. When insulin isn’t working properly, blood sugar levels can rise, leading to diabetes. Belly fat is thought to contribute to insulin resistance, and carrying extra weight around your middle is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Belly fat has also been linked to an increased risk of cancer, particularly cancers of the breast, colon, and rectum. Fat tissue produces estrogens, which can promote the growth of cancer cells. Additionally, fat cells can also lead to inflammation, which has been linked to an increased risk of cancer.
One is that abdominal fat cells release substances that increase inflammation throughout the body. This can damage blood vessels and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up on artery walls and restricts blood flow. Additionally, abdominal fat cells produce hormones that can lead to high blood pressure by causing the kidneys to retain fluid. Finally, belly fat also decreases levels of HDL cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol that helps remove LDL cholesterol from arteries. When levels of HDL cholesterol fall, it increases the risk of heart disease.
Sleep apnea is a condition in which breathing is interrupted during sleep. It can be caused by fat deposits around the neck and throat, which can block the airway and make it difficult to breathe. In addition, sleep apnea can also lead to fatigue and daytime drowsiness.